What is an SSL Certificate and Why Does Your Website Need It?
An SSL certificate is a must for any website that cares about its security. It brings more trust from the user, the web browser, and the search engine.
This article explains what an SSL certificate is, how it works, its benefits for SEO, and how to implement it on your website.
What is an SSL Certificate?
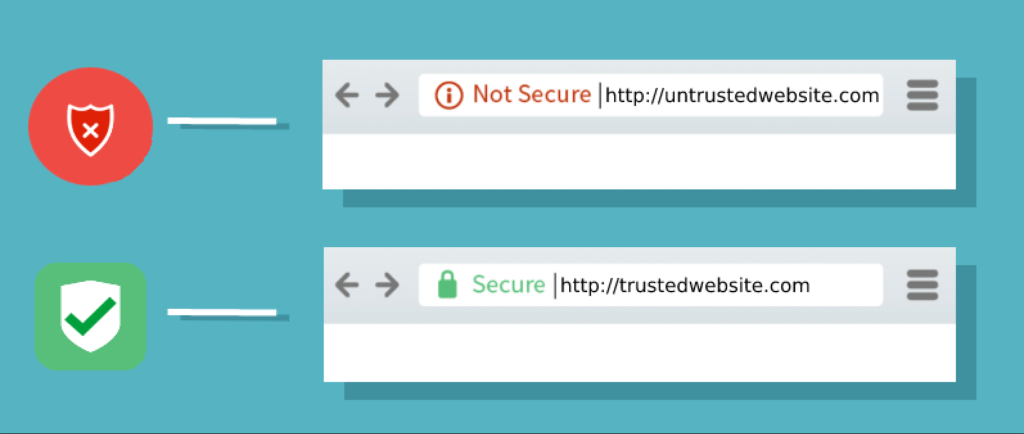
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer protocol, and it’s required for a website to have HTTPS encryption. This encryption provides secure data transfer between a server and a client.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) enables the web browser and the server to form a secure connection and protect the website’s sensitive data. SSL certificate adds the “S” in HTTPS, which stands for “Secure”.
What is a Server?
A server is a computer program or device responsible for providing services to another computer program by storing, sending, and receiving data.
In this case, the SSL server that issues an SSL certificate to the publisher exchanges data with the client server (user’s web browser) to ensure a secure connection without third-party interceptions.
The process of forming this connection between the client server and SSL server is called the SSL handshake.
TLS vs SSL?
TLS stands for Transport Layer Security, and it is a more upgraded and newer version of SSL. Therefore, TLS is more used and has replaced SSL, but SSL still is a more common term.
Both SSL and TSL are security protocols that verify data transfer between servers, systems, apps, and users.
How Does SSL Work?
SSLs work on public key infrastructure (PKI) to ensure security while information is being shared or transmitted.
This involves 2 cryptographic keys–the private key and the public key. They are used for decryption (information transformation into its original format–plaintext), and encryption (information transformation into a secure unreadable format–chipertext).
All the information from the client server is sent to the CA (certificate authority) for verification. CA is an independent body that validates the websites and issues SSL certificates.
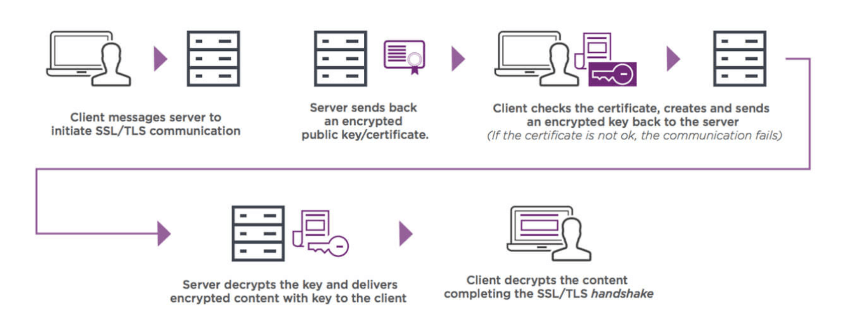
The SSL handshake consists of 5 main steps:
- When a user navigates to a website, his web browser first needs to verify the publishers’ web server’s identity. The web browser sends a message to the SSL server.
- The SSL server sends a certificate to the browser with encrypted public key data for verification.
- After the browser confirms the identity of the CA, it sends an encrypted message with the public key to the SSL server, which only the SSL server can decrypt with the private key.
- The SSL server decrypts the private key, sends encrypted content back to the web browser, and they agree on secure connection and specific session data details.
- The SSL handshake is completed, and the padlock icon appears in the browser’s search bar. Now the website’s browsing is safe and won’t be interrupted.
Source: Wikipedia
What information does an SSL certificate contain?
SSL certificate contains the following information:
- Domain name
- Issue and expiry date of the certificate
- CA details
- Public key and its algorithm (private key isn’t shared)
- Certificate Signature
- SSL version
- Thumbprint (a unique certificate identifier) and its algorithm (a hexadecimal string that portrays the identification)
Depending on the SSL certificate you obtain, it can also include information about your company and ownership.
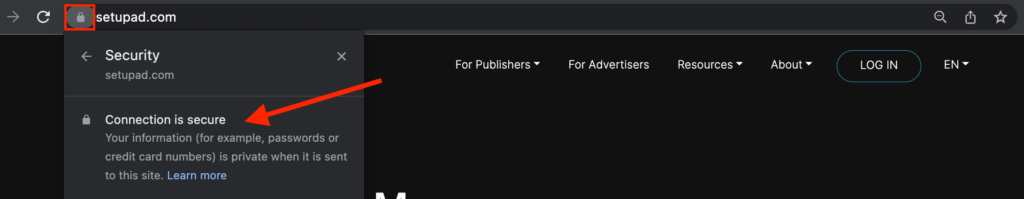
How to tell if my website has SSL?
There are 2 simple ways to check if your website has an SSL certificate:
- Your website should have the padlock icon in the browser’s search box.
- Your website should start with HTTPS, not HTTP.

Types of SSL Certificates
There are 3 types of SSL certificates:
- Single Domain–applies only to one domain (e.g., setupad.com, setupad.com/blog).
- Wildcard–applies to the main domain and all of its subdomains, which usually start with something different than the acronym “www”.

- Multi-domain–can be applied for multiple, different domains that don’t have to be subdomains.

Why Do Websites Need an SSL Certificate?
There are 4 main benefits of having an SSL certificate:
- User data safety and privacy. An SSL keeps user information secure, such as login details and personal information.
- Verified ownership. Having an SSL certificate proves that the site is legitimate and safe to use, especially if you own a higher level of validation on your SSL certificate (discussed below) because they contain additional information about the ownership of a website.
- Protection from malicious attacks. SSL certificate protects sites from interferences that can damage a website’s performance and from attackers that perform negative SEO attacks, such as website hacking.
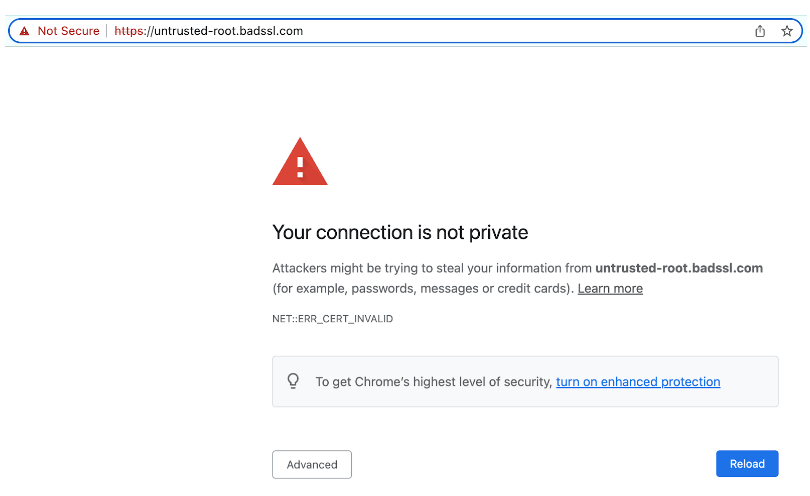
- Reputation. If your website doesn’t have an SSL certificate, web browsers like Google Chrome present a warning message to users, informing them the site isn’t secured. This dramatically impacts your rankings and overall reputation.
Which SSL Certificate Do You Need?
There are 3 types of validations for an SSL certificate. Depending on your website and the user data it processes, you may need a different type of validation for your SSL certificate.
- DV (Domain Validation) SSL–the cheapest and easiest SSL certificate to obtain for a quick launch of HTTPS. The website only has to prove to the CA that they own the domain, but no additional information about the owner is displayed on the certificate.
- OV (Organization Validation) SSL–is more trustworthy than a DV certificate but involves a more detailed evaluation. The CA will contact and investigate the website and display additional information on the certificate about the website owner.
- EV (Extended Validation) SSL–the most complicated and expensive SSL certificate to obtain. The CA will do a full investigation of the company to ensure that all the information about it is valid. These are the most trustful certificates and are especially important for sensitive user data websites.
The table below summarizes which SSL validation type is best suited for different websites.
| Usage | Recommended SSL certificate type | Example of SSL certificate issuer |
Websites that don’t conduct payments or collect sensitive data but need HTTPS to keep some user data private (e.g., blogs) | DV, OV | Let’s Encrypt |
| Websites that need to secure user login data, personal information, or documents | OV, EV | DigiCert |
| Websites that hold sensitive user information, conduct payments, and need a high level of security | EV | Comodo, DigiCert |
Does SSL increase SEO?
SSL certificate is one of the ranking factors for search engines, so having it is important for creating a good SEO strategy
Search engines want to provide a good user experience, including safety. Therefore, having HTTPS proves that your site is secure.
If you own the EV or OV SSL certificate, it also includes more information about your company, which helps to prove your authority and credibility. That’s beneficial for Google’s E-A-T principles.
How many websites have SSL?
SSL is the security standard that web browsers and search engines want to see on any website.
The recent data below shows that 79,2% of all the websites use the default HTTPs protocol.
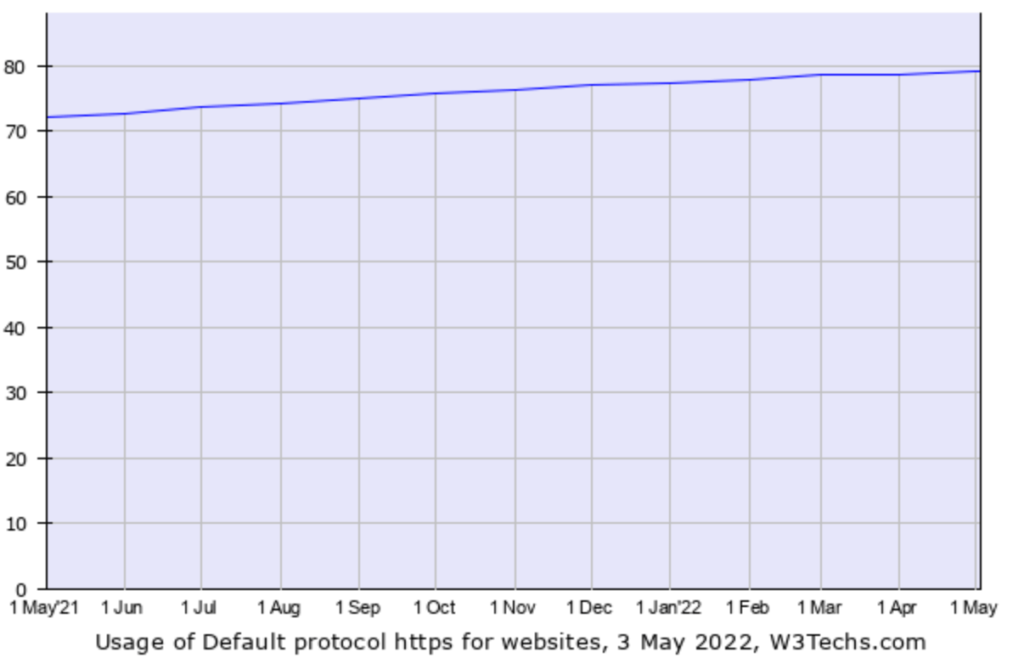
Source: W3Techs
How to Get an SSL Certificate?
To get an SSL certificate, you need to take the following steps:
- Generate the CSR on your server or an online CSR generator, such as OpenSSL CSR Wizard. You can check your website’s registration data on ICANN lookup before you create the CSR.
- Submit your CSR to the CA for validation and receive your SSL certificate.
- Now that you have your certificate, you need to install it on your server. You can do this through your hosting provider, for example, Bluehost or if you’re using a web hosting panel like cPanel, you can manually install and update the SSL certificate from there.
The signature of a trusted CA on your certificate is one of the most important parts for the browser to recognize that your certificate as valid.
How to update an existing SSL certificate?
To update an existing SSL certificate, the process is the same as getting a new one.
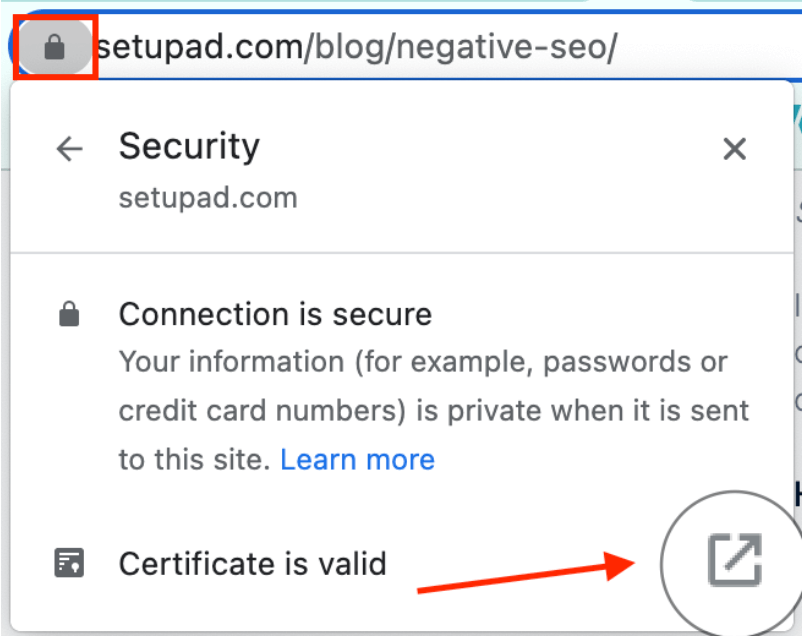
To check the SSL certificate’s expiration date, you need to:
- Click on the padlock icon in the browser’s search bar.
- Click on the expanding icon next to “Certificate is valid”.
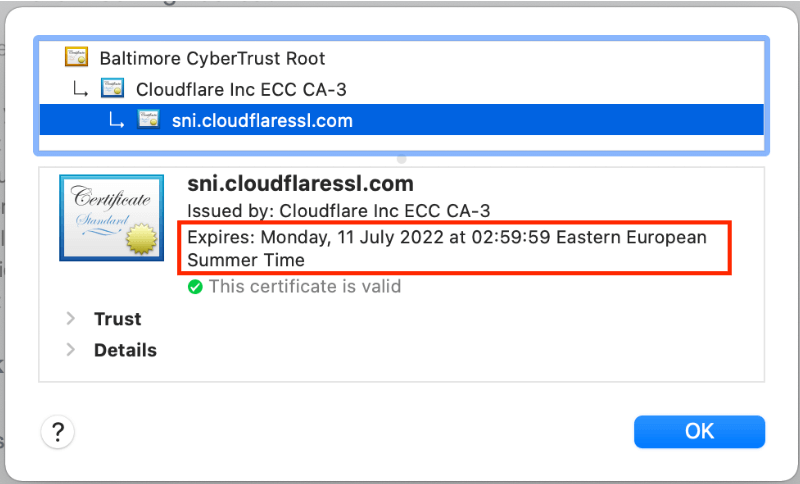
- Look for the expiration date in the certificate details.
During the SSL certificate update, your information will be renewed, which means that you’ll have to send a new CSR to the CA and fill up all the necessary details again.
Conclusion
As website attacks continue to increase, having an SSL certificate for your website is a necessary security standard.
It provides a good user experience and benefits your SEO performance, also granting your website’s data safety.
Make sure that you include an SSL certificate on your website and stay on the safe side!

